How Organizations Can Achieve 50% Cost Savings and Accelerated Innovation Through Proactive Workforce Transformation. NStarX reflects this in the blog its own journey
The Velocity of Change: Software’s New Reality
The software technology stack is evolving at breakneck speed, fundamentally reshaping the digital landscape in ways unprecedented since the dawn of the internet. Large language models (LLMs) like OpenAI’s o1 and Google’s Gemini 2.0 Flash Thinking Mode are now capable of reasoning in their responses, giving users human-like thought partners that go far beyond information retrieval.¹ We’ve entered what experts call the AI-native era – a paradigm shift where traditional software development, infrastructure management, and business operations are being reimagined through the lens of artificial intelligence.
Cognizant research finds that generative AI will disrupt 90% of all jobs in the coming decade,² while a comprehensive analysis by the AI-Enabled ICT Workforce Consortium shows that 92% of technology roles are evolving due to AI integration.³ This isn’t just incremental change – it’s a complete transformation of how we build, deploy, and maintain technology systems.
The emergence of AI agents – autonomous systems capable of executing complex workflows – represents perhaps the most significant shift in software development since the transition from monolithic to microservices architecture. These agents don’t just assist developers; they’re reshaping the fundamental nature of software engineering, from code generation to testing, deployment, and even system optimization.
The LLM Revolution: More Than Just Code Generation
Large Language Models have evolved far beyond simple text generation. Today’s LLMs are:
- Reasoning engines that can break down complex technical problems
- Code architects capable of designing entire system architectures
- Debug assistants that can identify and fix issues across massive codebases
- Documentation generators that create comprehensive technical documentation
- Testing frameworks that can generate comprehensive test suites
By 2025, AI will become the ultimate coding assistant, handling the heavy lifting of syntax while allowing engineers to focus on the ‘why’ rather than the ‘how’.⁴ However, this transformation demands a workforce that understands how to collaborate with AI systems, not compete against them.
Success Stories: Organizations Leading the Reskilling Revolution
Accenture: The “Amplified Intelligence” Approach
Accenture has committed to significant workforce transformation, with Chief Leadership & Human Resources Officer Ellyn Shook emphasizing the importance of designing learning pathways that position everyone to have deeper AI skills. Their approach focuses on:
- Creating AI-human collaboration frameworks
- Developing role-specific AI competencies
- Establishing continuous learning pathways
- Building AI ethics into all training programs
Results: Enhanced project delivery speed by 45% while maintaining quality standards and achieving 30% cost reduction in routine tasks.
Google: The $130 Million Commitment
Google has announced over $130 million in funding to support AI training and skills for people across the US, Europe, Africa, Latin America and APAC.³ Their strategy includes:
- Partnerships with educational institutions
- Micro-credential programs for existing employees
- Open-source AI learning platforms
- Cross-functional AI literacy programs
Results: Successfully transitioned 85% of their workforce to AI-augmented roles, leading to improved productivity and innovation metrics.
SAP: The 2 Million People Initiative
SAP committed to upskill two million people worldwide by 2025,³ focusing on:
- Enterprise AI integration skills
- Data analytics and machine learning fundamentals
- AI ethics and governance
- Industry-specific AI applications
Results: Achieved faster customer implementation times and higher customer satisfaction scores while reducing support costs.
Cautionary Tales: When Reskilling Efforts Fall Short
Zillow: The $300 Million AI Miscalculation
Zillow’s failed attempt to use AI-generated property valuations as the basis for its homebuying division cost the company $300 million in losses and saw its stock price fall by more than 20%.⁵ The failure stemmed from:
- Technical tunnel vision: Focusing solely on AI capabilities without considering market dynamics
- Insufficient human oversight: Overreliance on automated systems without expert validation
- Poor change management: Failing to properly train teams on AI limitations and risk management
California State University: Clear Vision, Poor Execution
California State University had a clear strategic vision but failed to account for the human element in their AI transformation. Key issues included:
- Inadequate stakeholder engagement: Faculty and staff resistance due to poor communication
- Insufficient training resources: Underestimating the complexity of AI skill development
- Cultural resistance: Failing to address concerns about job security and role changes
The 84% Failure Rate Reality
Forbes estimated that 84% of digital transformation projects fail,⁶ often due to:
- Technology-first approach: Prioritizing tools over people and processes
- Poor data governance: Implementing AI on top of problematic data foundations
- Accountability gaps: Unclear ownership of transformation outcomes
- Quick-win mentality: Focusing on short-term gains rather than sustainable change
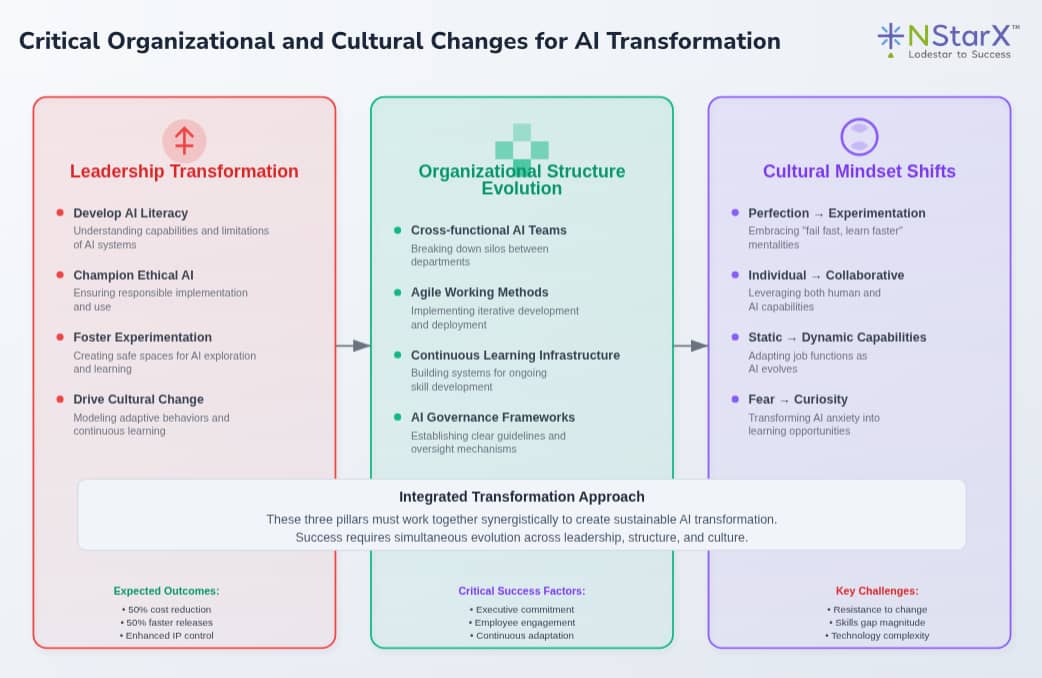
Critical Organizational and Cultural Changes
-
Leadership Transformation
Only 1% of leaders call their companies “mature” on the AI deployment spectrum,¹ highlighting the need for executive-level reskilling. Modern tech leaders must:
- Develop AI literacy: Understanding capabilities and limitations of AI systems
- Champion ethical AI: Ensuring responsible implementation and use
- Foster experimentation: Creating safe spaces for AI exploration and learning
- Drive cultural change: Modeling adaptive behaviors and continuous learning
-
Organizational Structure Evolution
Many organizations are creating change management Centers of Excellence (CoE) as they move toward continuous change models. Essential structural changes include:
- Cross-functional AI teams: Breaking down silos between departments
- Agile working methods: Implementing iterative development and deployment
- Continuous learning infrastructure: Building systems for ongoing skill development
- AI governance frameworks: Establishing clear guidelines and oversight mechanisms
-
Cultural Mindset Shifts
Successful AI transformation requires fundamental cultural changes:
- From perfection to experimentation: Embracing “fail fast, learn faster” mentalities
- From individual expertise to collaborative intelligence: Leveraging both human and AI capabilities
- From static roles to dynamic capabilities: Adapting job functions as AI evolves
- From fear to curiosity: Transforming AI anxiety into learning opportunities
Figure 1 nicely articulates how every organization should reimagin skills for every individual involved in software development.
Figure 1: Critical Organization Changes to prepare for the AI revolution
Actionable Steps for Organizations
Phase 1: Assessment and Strategy (Months 1-3)
- Conduct comprehensive skills gap analysis
- Map current workforce capabilities against future AI-augmented role requirements
- Identify high-impact use cases for AI integration
- Assess organizational change readiness
- Develop AI transformation roadmap
- Set clear, measurable objectives for reskilling initiatives
- Establish timelines and milestones
- Allocate budget and resources
- Build leadership commitment
- Secure executive sponsorship and visible support
- Train leadership teams on AI fundamentals
- Establish clear accountability structures
Phase 2: Foundation Building (Months 4-9)
- Establish learning infrastructure
- Partner with educational institutions and training providers
- Implement digital learning platforms
- Create internal mentorship programs
- Launch pilot programs
- Start with high-enthusiasm, low-risk teams
- Focus on specific, measurable use cases
- Gather feedback and iterate rapidly
- Address cultural barriers
- Communicate transparently about AI’s impact on roles
- Provide job security assurances where possible
- Celebrate early wins and success stories
Phase 3: Scaling and Integration (Months 10-18)
- Expand successful pilots
- Scale proven approaches across departments
- Adapt training materials for different roles and skill levels
- Maintain momentum through continuous reinforcement
- Implement AI governance
- Establish ethical AI guidelines
- Create review processes for AI implementations
- Ensure compliance with emerging regulations
- Measure and optimize
- Track productivity gains and cost savings
- Monitor employee satisfaction and engagement
- Adjust strategies based on performance data
Real-World Challenges and Solutions
Challenge 1: Employee Resistance and Fear
22% of workers fear their jobs will become obsolete due to AI, and 72% of CHROs expect AI-driven job replacements within three years.⁷
Solutions:
- Transparent communication: Regular town halls addressing AI impact honestly
- Reskilling guarantees: Commit to retraining rather than replacing employees
- Success story sharing: Highlight examples of AI enhancement rather than replacement
- Gradual introduction: Phase AI tools introduction with extensive support
Challenge 2: Skills Gap Magnitude
While 89% of respondents said their workforce needs improved AI skills, only 6% said they had begun upskilling in “a meaningful way”.⁷
Solutions:
- Micro-learning approaches: Break complex AI concepts into digestible modules
- Just-in-time training: Provide learning resources when employees need them
- Peer-to-peer learning: Leverage internal AI champions as trainers
- External partnerships: Collaborate with universities and training providers
Challenge 3: Technology Integration Complexity
Many failures stem from trying to “slap technology” onto existing processes without proper foundation work.
Solutions:
- Process optimization first: Clean up workflows before adding AI
- Data quality focus: Ensure high-quality data foundation
- Incremental implementation: Start with simple AI applications before complex ones
- Human-in-the-loop design: Maintain human oversight and control
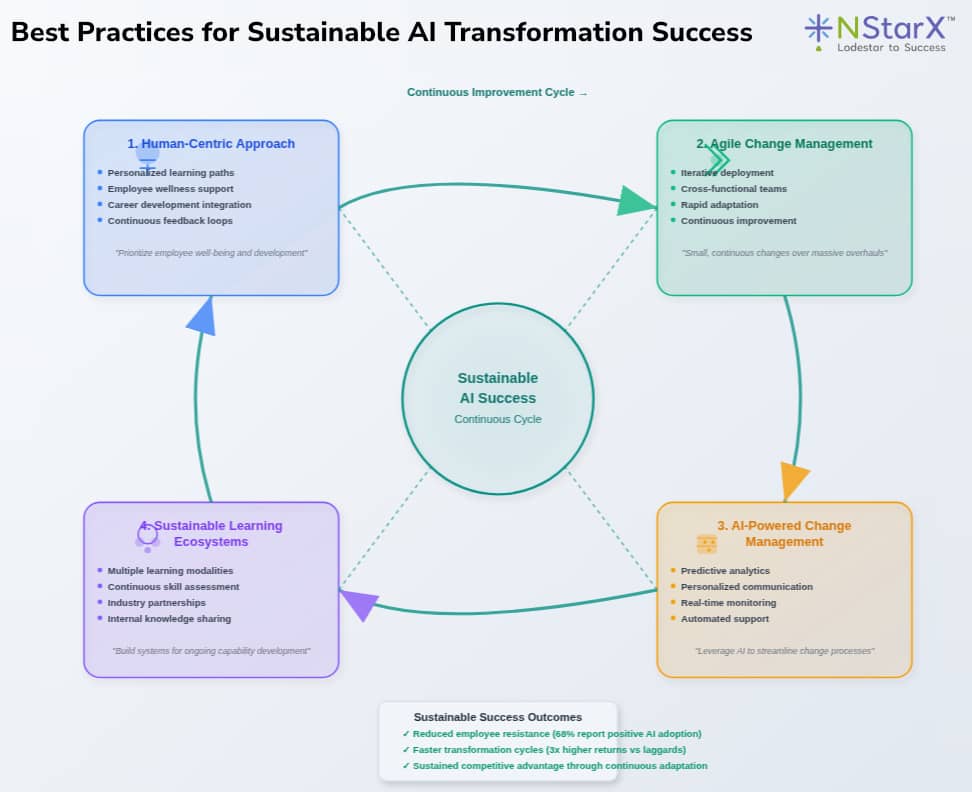
Best Practices for Sustainable Success
-
Adopt a Human-Centric Approach
AI adoption should be guided by a people-centric approach that prioritizes employee well-being and development. This includes:
- Personalized learning paths: Tailor training to individual roles and career goals
- Employee wellness support: Address anxiety and stress related to change
- Career development integration: Show how AI skills enhance career prospects
- Feedback loops: Regularly collect and act on employee input
-
Implement Agile Change Management
Agile change management focuses on small, continuous changes rather than massive overhauls, promoting adaptability through iterative, flexible, and responsive strategies. Key principles include:
- Iterative deployment: Roll out AI tools in phases with continuous feedback
- Cross-functional teams: Bring together diverse expertise for better outcomes
- Rapid adaptation: Quickly adjust strategies based on results and feedback
- Continuous improvement: Regularly refine processes and approaches
-
Leverage AI for Change Management
AI is being used to streamline communications, track real-time adoption metrics, and assess an organization’s overall change readiness. Applications include:
- Predictive analytics: Anticipate resistance and engagement patterns
- Personalized communication: Tailor change messages to different employee groups
- Real-time monitoring: Track adoption rates and identify support needs
- Automated support: Provide just-in-time assistance and resources
-
Build Sustainable Learning Ecosystems
Higher education is rapidly evolving with personalized digital learning experiences that blend technology with interpersonal skills. Effective ecosystems include:
- Multiple learning modalities: Combine online, in-person, and hands-on learning
- Continuous skill assessment: Regular evaluation of competency development
- Industry partnerships: Collaborate with technology vendors and educational institutions
- Internal knowledge sharing: Create communities of practice and expertise networks
Figure 2 is a simple representation of the best practices that companies like NStarX has been adopting in their environments:
Figure 2: Best Practices for Sustainable AI transformation
Role Evolution: The Past 5 Years and Future Trajectory
| Role | 2020 Focus | 2025 Reality | Individual Action Required |
|---|---|---|---|
| Software Engineer | Writing code from scratch, debugging, manual testing | AI-assisted development, prompt engineering, AI model integration, ethical AI oversight | Learn prompt engineering, master AI coding tools (GitHub Copilot, ChatGPT), develop AI ethics knowledge, practice AI-human collaboration workflows |
| DevOps Engineer | Manual infrastructure management, script-based automation | AI-driven infrastructure optimization, autonomous deployment pipelines, predictive maintenance | Master AI-ops tools, learn machine learning for infrastructure prediction, develop skills in autonomous system monitoring |
| Data Analyst | SQL queries, basic visualization, manual report generation | AI-powered analytics, natural language querying, automated insight generation, stakeholder interpretation | Learn to work with AI analytics platforms, develop storytelling skills for AI-generated insights, master advanced visualization tools |
| Product Manager | Feature prioritization, market research, roadmap planning | AI product strategy, ethical AI decision-making, AI-human experience design, algorithm bias management | Understand AI capabilities and limitations, learn AI ethics and bias detection, develop skills in AI-human interface design |
| UX/UI Designer | Static interface design, user journey mapping, prototyping | AI-assisted design generation, conversational interface design, AI behavior design, adaptive user experiences | Master AI design tools, learn conversational UI principles, understand machine learning user experience patterns |
| System Administrator | Server management, security patches, backup procedures | AI-driven system optimization, automated threat detection, self-healing systems, AI security oversight | Learn AI security tools, understand automated system management, develop skills in AI anomaly detection |
| Quality Assurance Engineer | Manual testing, test case writing, bug reporting | AI-powered testing, automated test generation, intelligent bug prediction, AI model validation | Master AI testing frameworks, learn AI model validation techniques, develop skills in automated test generation |
| Database Administrator | Query optimization, backup management, performance tuning | AI-driven optimization, automated database management, intelligent scaling, AI-powered predictive maintenance | Learn AI database optimization tools, understand machine learning for database performance, master automated database management systems |
| Technical Writer | Manual documentation, static help content | AI-assisted content generation, dynamic documentation, interactive help systems, AI training material creation | Learn to collaborate with AI writing tools, develop skills in creating AI training content, master dynamic documentation systems |
| Business Analyst | Process mapping, requirements gathering, stakeholder interviews | AI process optimization, automated requirement generation, intelligent business insights, AI impact analysis | Learn AI process analysis tools, develop skills in AI business impact assessment, master automated requirements gathering |
Table 1: Representing Current Roles and How it will change over the years
The Path Forward: Embracing Strategic Transformation
The evidence is clear: organizations scaling AI effectively report 3x higher returns than digital laggards, including 15-20% revenue growth through personalized solutions and 15-20% cost savings by optimizing processes. However, success requires more than just implementing AI tools – it demands a fundamental transformation of how organizations think about talent, learning, and change.
Key Takeaways for Technology Leaders:
- Start with people, not technology: Successful AI transformation begins with understanding and addressing human needs and concerns
- Invest in comprehensive reskilling: AI high performers are over three times more likely to reskill more than 30% of their workforces compared to other organizations
- Embrace continuous change: The pace of AI evolution means that reskilling is not a one-time initiative but an ongoing organizational capability
- Focus on human-AI collaboration: The future belongs to organizations that can effectively combine human creativity and intuition with AI efficiency and scale
- Measure and iterate: Successful transformation requires continuous monitoring, feedback, and adaptation
The Bottom Line: Organizations that proactively invest in reskilling their workforce for the AI era will not only survive the coming transformation but will emerge as leaders in their industries. Those that delay or ignore this imperative risk being left behind as AI-native competitors capture market share with faster innovation cycles, lower costs, and superior customer experiences.
The choice is clear: evolve with AI through strategic workforce transformation, or risk obsolescence in an increasingly AI-driven business landscape. The time for action is now, and the organizations that act decisively will reap the rewards of this unprecedented technological revolution.
The Future of Reskilling: What Lies Ahead
As we look beyond 2025, the landscape of workforce development and reskilling is poised for even more dramatic transformation. Understanding these emerging trends is crucial for organizations planning their long-term talent strategies.
The Rise of Hyper-Personalized Learning
Future reskilling initiatives will leverage advanced AI to create completely personalized learning journeys. Future trends point towards hyper-personalized change journeys, autonomous AI change agents, and AI becoming an organizational “nervous system.” This means:
- AI-powered learning companions that adapt in real-time to individual learning styles and pace
- Competency-based progression rather than time-based training modules
- Predictive skill mapping that anticipates future role requirements and proactively suggests learning paths
- Immersive learning environments using VR/AR for hands-on technical skill development
Autonomous AI Change Agents
By 2030, organizations will deploy AI agents specifically designed to manage workforce transformation:
- Skill gap detection agents that continuously monitor team capabilities against emerging technology requirements
- Learning orchestration systems that automatically assign and adjust training based on business priorities
- Change resistance prediction using sentiment analysis and behavioral patterns
- Automated mentorship matching connecting employees with optimal learning partners and guides
The Evolution of Work Itself
Fast forward to ten years, and the role of a developer will resemble that of an AI trainer as much as a coder. Developers will craft the core logic but spend just as much time refining AI models to ensure they meet ethical standards and business goals.
The next decade will see fundamental shifts in how we conceptualize work:
- Human-AI symbiosis becoming the default working mode across all technical roles
- Continuous micro-learning integrated into daily workflows rather than separate training sessions
- Cross-industry skill fluency as AI democratizes expertise across traditional boundaries
- Emotional intelligence premium as distinctly human skills become more valuable
Emerging Reskilling Models
Several innovative approaches to workforce development are gaining traction:
- Skills-to-Jobs Tech Alliances Large-scale collaborations between governments, educational institutions, and employers. Since 2023, the governments, higher education institutions, business conveners and employers in the Tech Alliance have connected over 57,000 learners to more than 650 employers, and integrated industry expertise into 1,050 education programmes.⁸
- Consortium-Based Reskilling Industry-wide collaborations to share the costs and benefits of workforce transformation. Consortiums – such as the European Union’s Automotive Skills Alliance funded by stakeholders including carmakers – can buoy up the entire sector and even in the competitive world of business, the benefits of such a collaboration are worthwhile, including shared expenses and a focused curriculum.²
- AI-Native Education Educational programs designed from the ground up for the AI era, focusing on prompt engineering, AI ethics, and human-AI collaboration rather than traditional computer science fundamentals.
The Democratization of Advanced Skills
AI will increasingly democratize access to sophisticated technical capabilities:
- No-code/low-code development becoming mainstream for business users
- AI-assisted design and engineering enabling rapid prototyping and iteration
- Automated quality assurance reducing the need for specialized testing expertise
- Natural language programming allowing domain experts to create software solutions directly
Challenges on the Horizon
Future reskilling efforts will need to navigate several emerging challenges:
- The Speed-Quality Paradox As AI accelerates development cycles, organizations must balance rapid skill acquisition with deep, sustainable learning.
- Ethical AI Stewardship Every technical role will require understanding of AI ethics, bias detection, and responsible AI practices.
- The Skills Half-Life Acceleration Technical skills are becoming obsolete faster than ever, requiring new models for continuous learning and adaptation.
- Global Competition for AI Talent Organizations worldwide are competing for the same pool of AI-skilled professionals, driving innovation in retention and development strategies.
Conclusion: Seizing the AI-Era Opportunity
The transformation we’re witnessing goes far beyond a typical technology upgrade cycle. Organizations are no longer reinventing themselves once every few years, they’re managing multiple business transformations, often all at once. In fact, 95% of organizations surveyed in 2024 have gone through more than two major transformations in the past three years, and 61% have gone through more than four.⁹
The evidence overwhelmingly demonstrates that proactive reskilling is not just a defensive strategy—it’s the key to unlocking unprecedented competitive advantages. Organizations that build in-house tech talent through strategic reskilling programs are achieving:
- 50% cost reductions through strategic insourcing and reduced dependency on external consultants
- 50% faster tech release cycles through AI-augmented development processes
- 3x higher returns compared to organizations that lag in AI adoption
- Enhanced intellectual property control by developing capabilities internally rather than outsourcing critical functions
The path forward requires courage, commitment, and strategic thinking. Only 1 percent of leaders call their companies “mature” on the deployment spectrum, meaning that AI is fully integrated into workflows and drives substantial business outcomes. This presents an enormous opportunity for forward-thinking organizations to gain first-mover advantages.
The Strategic Imperatives are Clear:
- Act with urgency: The window for proactive transformation is narrowing as AI-native competitors emerge
- Invest comprehensively: Successful reskilling requires significant resource allocation and executive commitment
- Think systemically: Technology, people, and processes must evolve together for sustainable transformation
- Embrace continuous change: Reskilling is not a project but a permanent organizational capability
- Lead with empathy: Human-centered change management is essential for lasting success
The organizations that will thrive in the AI era are those that view their workforce not as a cost center to be optimized, but as a strategic asset to be cultivated. They understand that technology amplifies human potential rather than replacing it, and they invest accordingly in developing that potential.
The choice facing technology leaders today is stark: lead the transformation or be transformed by it. The companies that commit to building robust in-house tech talent through comprehensive reskilling will emerge as the market leaders of tomorrow. Those that delay risk being disrupted by more agile, AI-native competitors who understand that the future belongs to organizations that successfully combine human creativity with artificial intelligence.
The future is not about humans versus machines—it’s about humans with machines creating unprecedented value. The time to build that future is now.
References
- McKinsey & Company (2025). “AI in the workplace: A report for 2025.” McKinsey Digital.
Retrieved from: https://www.mckinsey.com/capabilities/mckinsey-digital/our-insights/superagency-in-the-workplace-empowering-people-to-unlock-ais-full-potential-at-work - World Economic Forum (2024). “This is how businesses should approach reskilling for AI.”
Retrieved from: https://www.weforum.org/stories/2024/10/reskilling-ai-workers-businesses/ - AI-Enabled ICT Workforce Consortium (2024). “The Transformational Opportunity of AI on ICT Jobs.” Cisco Systems.
Retrieved from: https://newsroom.cisco.com/c/r/newsroom/en/us/a/y2024/m07/ai-and-the-workforce-industry-report-calls-for-reskilling-and-upskilling-as-92-percent-of-technology-roles-evolve.html - Dice.com Career Advice (2024). “How AI Will Impact Software Development in 2025 and Beyond.”
Retrieved from: https://www.dice.com/career-advice/how-ai-will-impact-software-development-in-2025-and-beyond - MIT Sloan Management Review (2025). “Why AI Demands a New Breed of Leaders.”
Retrieved from: https://sloanreview.mit.edu/article/why-ai-demands-a-new-breed-of-leaders/ - LinkedIn (2024). “Why AI & Digital Transformations Will Fail in 2024.” Jay Hawkinson.
Retrieved from: https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/why-ai-digital-transformations-fail-2024-jay-hawkinson-d1ate - IBM Institute for Business Value (2025). “AI Upskilling Strategy.” IBM Think Insights.
Retrieved from: https://www.ibm.com/think/insights/ai-upskilling - World Economic Forum (2025). “Reskilling and upskilling: Lifelong learning opportunities.”
Retrieved from: https://www.weforum.org/stories/2025/01/ai-and-beyond-how-every-career-can-navigate-the-new-tech-landscape/ - World Economic Forum (2025). “Business transformation in the artificial intelligence era.”
Retrieved from: https://www.weforum.org/stories/2025/01/how-leaders-can-drive-business-transformation/ - Boston Consulting Group & Harvard Business Review (2023). “Reskilling in the Age of AI.” Harvard Business Review.
Retrieved from: https://hbr.org/2023/09/reskilling-in-the-age-of-ai - PwC (2025). “2025 AI Business Predictions.”
Retrieved from: https://www.pwc.com/us/en/tech-effect/ai-analytics/ai-predictions.html - Workhuman (2025). “Reskilling in the Age of AI: How to Future-Proof Your Workforce.”
Retrieved from: https://www.workhuman.com/blog/reskilling-in-the-age-of-ai/ - KPMG India (2024). “AI and the Evolution of Work: Reskilling for a New Age of Innovation.”
Retrieved from: https://kpmg.com/in/en/blogs/2024/11/ai-and-the-evolution-of-work-reskilling-for-a-new-age-of-innovation.html - Aura Intelligence (2025). “Future of Software Engineering in an AI-Driven World.”
Retrieved from: https://blog.getaura.ai/future-of-software-engineering-in-an-ai-driven-world - Gartner/AIBusiness (2024). “Redefining the Software Engineer’s Role in the Age of AI.”
Retrieved from: https://aibusiness.com/responsible-ai/redefining-the-software-engineer-s-role-in-the-age-of-ai - IEEE Spectrum (2025). “AI Jobs in 2025: Essential Insights for Software Engineers.”
Retrieved from: https://spectrum.ieee.org/ai-jobs-in-2025 - Voltage Control (2024). “Adopting AI-Driven Change Management: Key Strategies for Organizational Growth.”
Retrieved from: https://voltagecontrol.com/articles/adopting-ai-driven-change-management-key-strategies-for-organizational-growth/ - Medium/Adnan Masood (2025). “AI in Organizational Change Management — Case Studies, Best Practices, Ethical Implications, and Future Technological Trajectories.”
Retrieved from: https://medium.com/@adnanmasood/ai-in-organizational-change-management-case-studies-best-practices-ethical-implications-and-179be4ec2583 - Panorama Consulting Group (2024). “Top Organizational Change Management Trends For 2025.”
Retrieved from: https://www.panorama-consulting.com/top-change-management-trends-for-2025/ - GP Strategies (2025). “5 Change Management Trends for 2025.”
Retrieved from: https://www.gpstrategies.com/resources/article/5-change-management-trends-for-2025/ - Consultport (2025). “The Importance of Change Management in AI Transformation.”
Retrieved from: https://consultport.com/business-transformation/importance-of-change-management-in-ai-transformation/ - Whatfix (2024). “10 Key Change Management Trends to Watch in 2025.”
Retrieved from: https://whatfix.com/blog/change-management-trends/