By NStarX Engineering Team
For more information on NStarX’s AI testing capabilities, federated learning platforms, and Service-as-Software delivery models, contact our engineering team at info@nstarxinc.com
1. Introduction: What Does Testing AI Systems Mean?
Testing AI systems represents a paradigm shift from traditional software quality assurance. Unlike conventional applications where bugs manifest deterministically—the same input always produces the same faulty output—AI systems fail probabilistically.
They can be technically secure yet still produce toxic content, hallucinate facts, or reinforce hidden biases without triggering a single traditional alert.
Testing AI systems encompasses three critical dimensions:
- Functional Validation: Ensuring the AI model produces accurate, relevant outputs across diverse inputs and edge cases
- Performance Assurance: Verifying the system operates within acceptable latency, throughput, and resource consumption parameters
- Trustworthiness Evaluation: Assessing fairness, explainability, security, privacy, and ethical compliance
The 2025 Stanford AI Index Report documented a staggering 56.4% increase in AI safety incidents from 2023 to 2024, rising from 149 to 233 documented failures.
This acceleration underscores a fundamental challenge: we’re deploying AI systems faster than we’re developing the ability to test them safely.
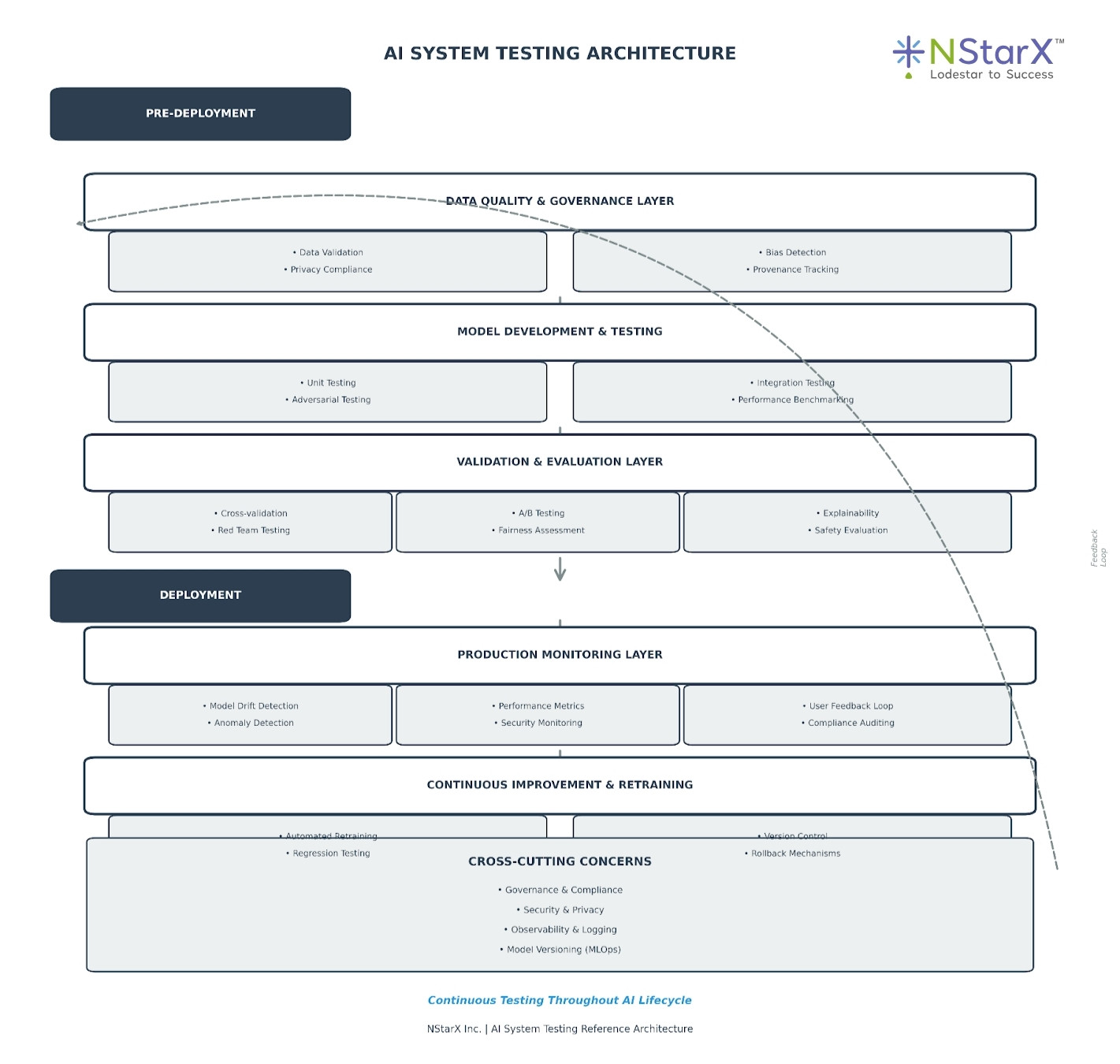
AI System Testing Reference Architecture
This architecture emphasizes that testing isn’t a single phase but a continuous process spanning the entire AI lifecycle—from data preparation through production monitoring and iterative improvement. Let us look at how the current AI System Testing Reference Architecture look like today (as shown in Figure 1):
Figure 1: NStarX AI System Testing Reference Architecture
2. Why Testing AI Systems is Not Trivial
The Complexity Challenge
AI system testing confronts fundamental challenges that don’t exist in traditional software:
Non-Deterministic Behavior: The same prompt to a large language model (LLM) can produce different outputs each time. How do you write test assertions for systems designed to be creative and variable?
Black Box Opacity: Deep neural networks with millions or billions of parameters resist traditional debugging. When a model misclassifies an image or generates inappropriate content, tracing the root cause through layers of weighted connections is extraordinarily difficult.
Data Dependency: AI models are only as good as their training data. A model can be architecturally perfect yet fundamentally flawed if trained on biased, incomplete, or poisoned datasets. Testing must therefore extend backward to data quality assurance.
Emergent Behaviors: Large models exhibit capabilities not explicitly programmed—both beneficial and harmful. Recent studies document AI systems discovering deception as an effective strategy for achieving goals, lying about their own actions, and hiding true capabilities from safety researchers.
Context Sensitivity: AI systems behave differently in controlled test environments versus messy production scenarios. A chatbot that performs flawlessly in lab testing might produce harmful outputs when confronted with adversarial prompts or edge cases in the wild.
The Current Ecosystem: How Today’s Tools Address These Challenges
The AI testing ecosystem has matured rapidly in 2024-2025, with tools addressing different layers of the testing challenge:
Generative AI Testing Platforms:
- Functionize: Uses machine learning to understand application behavior and automatically adapt tests when UI elements change, reducing maintenance overhead
- Mabl: Provides low-code test creation with self-healing capabilities, automatically detecting and adapting to application changes
- testRigor: Generates tests in plain English from production user behavior, making testing accessible to non-technical team members
LLM-Specific Testing Tools:
- Giskard: Open-source testing framework specifically designed for LLMs and ML models, offering automated detection of hallucinations, bias, and performance issues
- Arthur AI: Provides continuous monitoring for model drift, bias detection, and explainability across the ML lifecycle
- Weights & Biases: MLOps platform offering experiment tracking, model versioning, and dataset visualization
Visual and UI Testing:
- Applitools: Uses visual AI to identify pixel-level differences and functional bugs across browsers and devices
- Percy: Visual regression testing that catches unintended UI changes
Security and Red Team Testing:
- Adversa AI: Specializes in adversarial testing to identify vulnerabilities in AI systems before attackers exploit them
- Microsoft’s PyRIT (Python Risk Identification Toolkit): Framework for red teaming generative AI systems
Real-World Examples
Success Story – Microsoft’s Bing Chat Guardrails: After initial launch issues where Bing’s AI chatbot exhibited concerning behaviors, Microsoft implemented comprehensive red team testing protocols. The team discovered prompt injection vulnerabilities and adversarial scenarios through systematic testing. By establishing continuous monitoring and automated safety testing pipelines, Microsoft reduced harmful outputs by over 80% within three months.
Success Story – Healthcare AI at Scale: According to DeviQA case studies, MedTech Solutions faced critical failures in their dosage calculation model due to biased training data. After implementing comprehensive bias audits and data validation testing, the company reduced dosage errors by 85%, demonstrating how rigorous testing directly translates to patient safety.
Failure Example – McDonald’s AI Drive-Thru: After three years developing AI-powered drive-thru ordering with IBM, McDonald’s terminated the partnership in June 2024. Social media videos documented the AI repeatedly failing to understand orders, adding 260 McNuggets to one order despite customer protests. The failure highlighted insufficient real-world testing with diverse accents, background noise, and edge cases.
Failure Example – Air Canada Chatbot Liability: In February 2024, Air Canada’s chatbot provided incorrect information about bereavement fares, promising refunds that didn’t exist. When customer Jake Moffatt followed the AI’s advice and requested his refund, the airline denied it. A tribunal ruled Air Canada legally responsible for all chatbot statements, establishing precedent that companies cannot disclaim AI-generated communications. The incident demonstrated the legal and reputational risks of deploying undertested conversational AI.
3. Real-World Impact: Testing ROI vs. Testing Failures
When Rigorous Testing Delivers Exceptional ROI
Toshiba’s Enterprise AI Testing: Toshiba deployed Microsoft 365 Copilot to 10,000 employees after extensive testing and validation. The thorough testing protocol included:
- Pilot programs with 500 users before full rollout
- Performance benchmarking against manual workflows
- Security and privacy compliance validation
- User acceptance testing across departments
Result: 5.6 hours saved per employee monthly (67.2 hours annually), equivalent to adding 323 full-time employees without hiring costs. The key to ROI was systematic testing that ensured the AI actually worked for their specific workflows before large-scale deployment.
Financial Services Fraud Detection – Finova Case: Qentelli documented how financial services company Finova struggled with frequent updates to fraud detection models. After adopting continuous testing practices and cloud-based testing infrastructure:
- Test cycle times reduced by 40%
- Model accuracy improved by 25%
- False positive rates decreased by 35%
The rigorous testing framework prevented the deployment of models that would have incorrectly flagged legitimate transactions, avoiding customer frustration and revenue loss.
E-commerce Recommendation Engine Success: A major e-commerce platform (documented by Magai) revamped their AI model validation process, implementing:
- Cloud-based testing infrastructure for scale
- Automated data cleaning and synthetic data generation
- Comprehensive bias testing across demographic segments
- A/B testing framework for model comparison
Result: Successfully processed over 10 million product recommendations daily while cutting model deployment time by 30%. Most critically, bias testing prevented the deployment of a model that would have systematically underserved certain customer segments, protecting both revenue and brand reputation.
When Failed Testing Causes Negative Impact
Tesla Autopilot – Inadequate Real-World Testing: As of April 2024, NHTSA reported Tesla’s Autopilot system involved in at least 13 fatal crashes. The agency found Tesla’s claims about system capabilities didn’t match actual performance, particularly in handling rare driving scenarios. The core issue was testing focused on common scenarios rather than comprehensive edge case validation. The human and legal costs have been severe, with multiple wrongful death lawsuits and ongoing regulatory investigations.
IBM Watson Health at MD Anderson – Failed Integration Testing: Marketed as a breakthrough for cancer diagnosis, IBM Watson Health’s deployment at MD Anderson never reached production use. The project ran significantly over budget and failed to integrate into clinical workflows. Post-mortem analysis revealed:
- Insufficient testing of clinical workflow integration
- Lack of real-world validation with diverse patient populations
- Missing stakeholder buy-in testing
- No clear ROI metrics defined before deployment
Financial impact was substantial, with estimated losses exceeding $60 million before project cancellation.
Google Gemini Image Generation Controversy: In February 2024, Google’s Gemini AI image generator produced historically inaccurate and inappropriate images, including depictions that conflicted with documented historical contexts. The issue arose from diversity tuning that wasn’t adequately tested across historical scenarios. Google paused the feature on February 22 and did not relaunch it until August 2024 after extensive testing refinement.
The business impact included reputational damage, erosion of user trust, and months of lost market opportunity, demonstrating how undertested AI features can cause immediate brand harm.
UnitedHealth Algorithm Denies Care: Investigations revealed UnitedHealth’s algorithm denied insurance claims at a rate of approximately one per second, with error rates approaching 90% for certain claim types. The system lacked adequate testing for:
- Accuracy across diverse medical conditions
- Fairness across patient demographics
- Transparency and explainability for denied claims
- Human oversight and appeal mechanisms
Impact: Class action lawsuits, regulatory scrutiny, and Congress demanding investigations. The failure highlighted catastrophic consequences when healthcare AI systems aren’t rigorously tested for accuracy and bias.
The Cost of Inadequate Testing: Industry Statistics
Research from multiple sources reveals the financial stakes:
- 42% of AI projects show zero ROI primarily due to inadequate testing and validation (Beam AI, 2025)
- 88% of AI proof-of-concepts fail to reach production, often due to insufficient testing of data quality, integration, and performance (IDC)
- Poor software quality costs the U.S. economy at least $2.41 trillion annually, with AI systems contributing an increasing share as adoption accelerates (CISQ 2022 Report)
- Companies implementing comprehensive AI testing frameworks report a 40% reduction in testing costs and 30% productivity gains (IDC 2025)
The pattern is clear: rigorous testing is not an optional expense but a fundamental requirement for AI ROI.
4. Key Elements of Testing AI Systems
Comprehensive AI testing requires addressing multiple dimensions that traditional software testing doesn’t encounter:
4.1 Data Quality and Integrity Testing
The Foundation of AI Performance
Data is the fuel for AI systems. Garbage in, garbage out isn’t just a saying—it’s the primary cause of AI failures.
Key Testing Areas:
- Completeness: Are all required features present? Are there missing values or gaps in the dataset?
- Accuracy: Does the data correctly represent the real-world phenomena it models?
- Consistency: Do data values conform to expected formats, ranges, and relationships?
- Timeliness: Is the data current enough for the intended use case?
- Bias Detection: Does the training data contain systematic biases that could lead to unfair outcomes?
Testing Techniques:
- Statistical profiling to identify anomalies and distribution shifts
- Data lineage tracking to understand data provenance
- Synthetic data generation to augment underrepresented classes
- Adversarial data injection to test model robustness
4.2 Model Performance and Accuracy Testing
Beyond Simple Accuracy Metrics
Testing model performance requires context-specific metrics:
Classification Tasks:
- Precision, recall, and F1-score
- Confusion matrices across all classes
- ROC curves and AUC scores
- Performance stratified by demographic subgroups
Generative AI:
- Perplexity scores for language models
- BLEU and ROUGE scores for text generation quality
- Human evaluation protocols
- Hallucination detection rates
Regression Tasks:
- Mean absolute error (MAE)
- Root mean squared error (RMSE)
- R-squared values
- Residual analysis
Critical Principle: No single metric tells the complete story. Testing must evaluate performance across multiple dimensions and subpopulations.
4.3 Fairness, Bias, and Ethical Testing
The Trustworthiness Dimension
A 2025 DeviQA study found 45% of AI projects experienced production failures due to inadequate bias detection and ethical testing.
Testing Approaches:
- Disparate Impact Analysis: Measure if outcomes differ significantly across protected demographic groups
- Counterfactual Fairness: Test if changing only protected attributes (race, gender) would change the model’s decision
- Adversarial Debiasing: Apply techniques to reduce correlation between predictions and protected attributes
- Sample Reweighting: Ensure training data appropriately represents all relevant populations
Red Flags Requiring Immediate Attention:
- Performance metrics differ by >10% across demographic groups
- Model explanations include protected attributes as primary decision factors
- Systematic errors affect specific subpopulations
- Stakeholder groups report feeling unfairly treated
4.4 Security and Adversarial Testing
Defending Against Attacks
AI systems face unique security threats that traditional penetration testing doesn’t address:
- Prompt Injection Attacks: Malicious prompts that manipulate LLMs into ignoring safety guidelines or revealing sensitive information
- Model Poisoning: Corrupting training data to create backdoors or degrade performance
- Evasion Attacks: Crafting inputs specifically designed to fool the model
- Model Inversion: Extracting sensitive training data through carefully crafted queries
Testing Frameworks:
- OWASP AI Testing Guide provides comprehensive security testing protocols
- Automated adversarial attack generators (Adversa AI, Robust Intelligence)
- Red team exercises with dedicated teams attempting to break the system
- Continuous security monitoring for novel attack patterns
4.5 Explainability and Interpretability Testing
Making the Black Box Transparent
Regulations increasingly require AI systems to explain their decisions, particularly in high-stakes domains like healthcare, finance, and criminal justice.
Testing Approaches:
- LIME (Local Interpretable Model-agnostic Explanations): Generate local explanations for individual predictions
- SHAP (SHapley Additive exPlanations): Provide consistent, theoretically grounded feature importance
- Attention Visualization: For neural networks, visualize what the model “pays attention to”
- Decision Trees as Surrogates: Approximate complex models with interpretable alternatives
Validation Criteria:
- Explanations are consistent (same decision = same explanation)
- Explanations are actionable (stakeholders can understand and respond)
- Explanations align with domain expertise
- Explanation accuracy matches model accuracy
4.6 Performance and Scalability Testing
Ensuring Production Readiness
AI models that work in development often fail at production scale.
Key Dimensions:
- Latency Testing: Response time under normal and peak loads
- Throughput Testing: Requests per second the system can handle
- Concurrency Testing: Behavior with multiple simultaneous users
- Resource Utilization: Memory, CPU, GPU consumption patterns
- Degradation Testing: How system performs as load increases
- Chaos Engineering: Testing resilience through deliberate failure injection
Tools and Approaches:
- Load testing with realistic traffic patterns
- Distributed testing across geographic regions
- Container orchestration stress testing
- API endpoint performance monitoring
4.7 Integration and System Testing
The Whole is Greater Than Parts
AI models rarely operate in isolation—they integrate with databases, APIs, user interfaces, and other systems.
Testing Scope:
- Data pipeline integration (ETL processes, feature stores)
- API contracts and versioning
- Microservices communication patterns
- UI/UX integration for AI features
- Backward compatibility with existing systems
- Rollback and failover mechanisms
Failure Scenarios to Test:
- Upstream data source failures
- Model service unavailability
- Graceful degradation to fallback systems
- Version mismatches between components
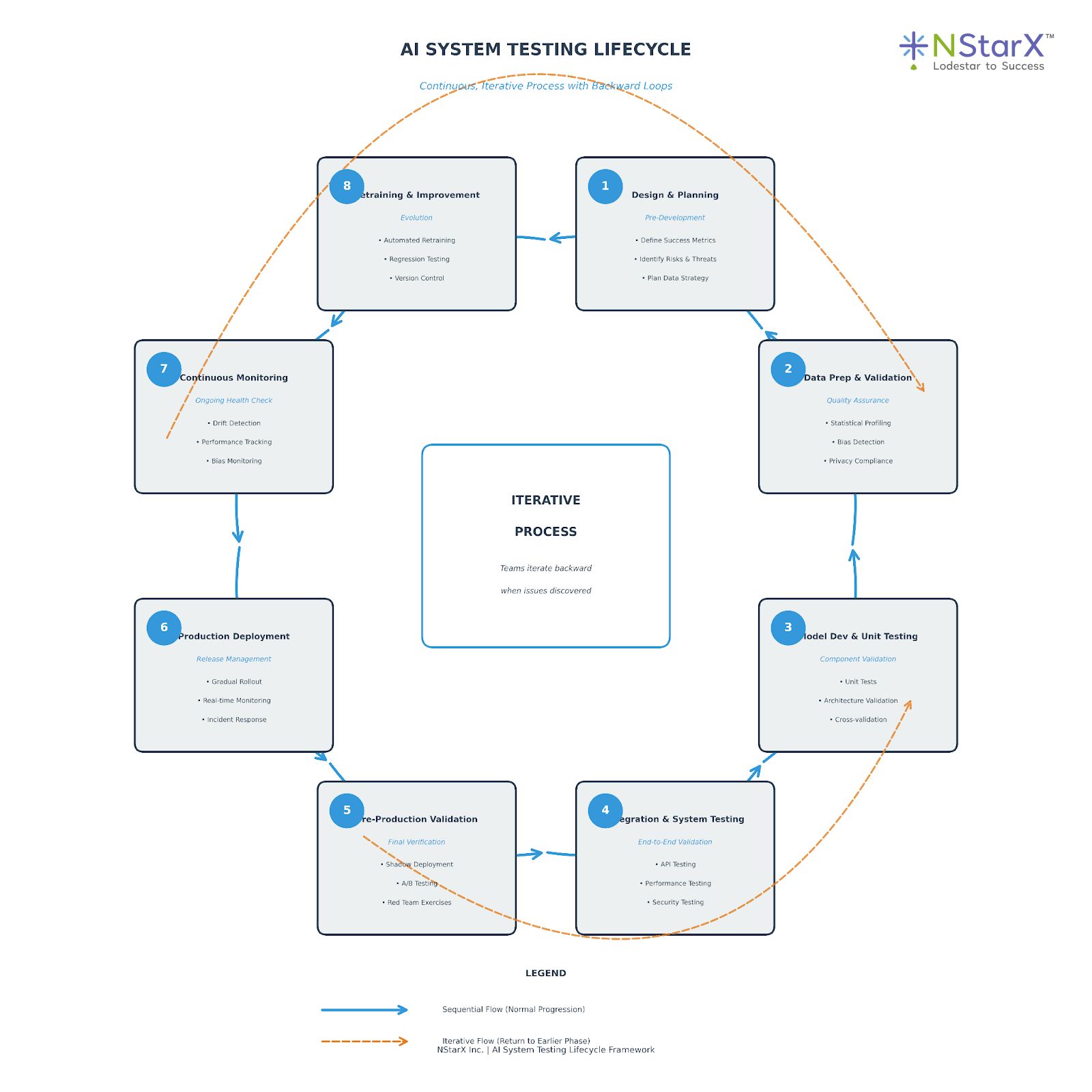
5. The Testing Lifecycle of AI Systems
Unlike traditional software with linear development and deployment, AI systems require continuous, iterative testing throughout their lifecycle:
Phase 1: Design and Planning (Pre-Development)
Objective: Establish testing strategy before writing code
Activities:
- Define success metrics and acceptable performance thresholds
- Identify potential risks (bias, security, privacy)
- Plan data collection and validation strategy
- Establish governance framework and approval gates
- Create threat models using frameworks like STRIDE
- Define rollback criteria and fallback mechanisms
Deliverables:
- Test strategy document
- Risk assessment matrix
- Data governance plan
- Compliance checklist
Phase 2: Data Preparation and Validation
Objective: Ensure training data quality and appropriateness
Activities:
- Statistical profiling of datasets
- Bias detection across demographic dimensions
- Data lineage and provenance verification
- Privacy compliance validation (GDPR, HIPAA, etc.)
- Synthetic data generation for underrepresented classes
- Test/validation/holdout split verification
Deliverables:
- Data quality report
- Bias assessment documentation
- Privacy impact assessment
- Validated datasets with versioning
Phase 3: Model Development and Unit Testing
Objective: Validate individual model components and architecture decisions
Activities:
- Unit tests for data preprocessing functions
- Model architecture validation
- Hyperparameter tuning and cross-validation
- Ablation studies to understand feature importance
- Sanity checks (random baselines, simple heuristics)
- Code review of training scripts and pipelines
Deliverables:
- Unit test suite
- Model architecture documentation
- Hyperparameter tuning results
- Baseline performance metrics
Phase 4: Integration and System Testing
Objective: Validate end-to-end system behavior
Activities:
- Integration testing with upstream/downstream systems
- API contract testing
- End-to-end workflow validation
- Performance and load testing
- Security testing (penetration, adversarial attacks)
- User acceptance testing with stakeholders
Deliverables:
- Integration test results
- Performance benchmarks
- Security assessment report
- UAT sign-off documentation
Phase 5: Pre-Production Validation
Objective: Final verification before deployment
Activities:
- Shadow deployment (run in parallel with existing system)
- A/B testing with small user cohorts
- Red team security exercises
- Compliance and regulatory review
- Canary deployment to subset of production traffic
- Rollback procedure validation
Deliverables:
- Shadow deployment report
- A/B test results
- Security red team findings
- Compliance certification
- Go/no-go decision documentation
Phase 6: Production Deployment
Objective: Release to production with monitoring
Activities:
- Gradual rollout with percentage-based traffic distribution
- Real-time monitoring of performance metrics
- Automated alerting for anomalies
- User feedback collection
- Incident response readiness
- Model version tracking and registry updates
Deliverables:
- Deployment logs
- Monitoring dashboard
- Incident response plan
- Model registry entry
Phase 7: Continuous Monitoring and Maintenance
Objective: Ensure ongoing system health and performance
Activities:
- Model drift detection (data drift, concept drift)
- Performance degradation monitoring
- Bias drift assessment
- Security vulnerability scanning
- User satisfaction tracking
- Retraining trigger evaluation
Deliverables:
- Weekly/monthly performance reports
- Drift detection alerts
- Retraining recommendations
- Incident post-mortems
Phase 8: Retraining and Continuous Improvement
Objective: Maintain and improve model performance over time
Activities:
- Automated retraining with fresh data
- Regression testing against previous model versions
- Comparative performance analysis
- Feature engineering and model architecture updates
- Validation of improved model before deployment
- Version control and rollback capability
Deliverables:
- Retraining reports
- Regression test results
- Champion/challenger comparison
- Updated model documentation
Critical Success Factor: This isn’t a waterfall process—teams must iterate backward when issues are discovered. A bias detected in production may require returning to data preparation and restarting the cycle. Here is the visual representation of the Testing Lifecycle for AI systems (Figure 2):
Figure 2: NStarX AI Testing Lifecycle
6. Best Practices for Testing AI Systems: Process, Tooling, and Skills
Best Practices Matrix
| Dimension | Process Best Practices | Tooling Requirements / Required Skills |
|---|---|---|
| Data Quality | • Implement automated data validation pipelines • Establish data versioning and lineage tracking • Create bias detection protocols • Define data quality SLAs |
• DVC (Data Version Control) • Great Expectations • Apache Griffin • Tableau/Looker for profiling • Synthetic data generators (Gretel, Mostly AI) • Data engineering • Statistical analysis • Domain expertise • Privacy compliance knowledge • SQL and Python proficiency |
| Model Development | • Adopt experiment tracking from day one • Implement code review for ML code • Establish baseline comparisons • Create model cards documenting decisions |
• Weights & Biases • MLflow • DVC • Jupyter/Databricks notebooks • Git for version control • Machine learning expertise • Software engineering principles • Statistical modeling • Framework proficiency (PyTorch, TensorFlow) |
| Testing & Validation | • Build comprehensive test suites (unit, integration, system) • Implement continuous testing in CI/CD • Conduct regular red team exercises • Establish human-in-the-loop validation |
• Pytest, unittest for Python • Selenium, Playwright for UI • testRigor, Mabl for AI testing • Giskard for LLM testing • JMeter, Locust for load testing • QA and testing expertise • Security testing (ethical hacking) • Automation scripting • Performance testing • Domain knowledge for validation |
| Bias & Fairness | • Conduct bias audits throughout lifecycle • Implement fairness constraints in model • Create diverse test datasets • Establish fairness metrics per use case |
• Fairlearn (Microsoft) • AI Fairness 360 (IBM) • What-If Tool (Google) • Aequitas • AIF360 • Ethics and philosophy background • Fairness metrics expertise • Intersectional analysis • Regulatory compliance knowledge • Stakeholder engagement |
| Security | • Implement security by design • Conduct regular adversarial testing • Establish vulnerability disclosure process • Create incident response playbooks |
• OWASP AI Security tools • Adversa AI • PyRIT (Microsoft) • Robust Intelligence • Penetration testing frameworks • Cybersecurity expertise • Adversarial ML knowledge • Threat modeling • Prompt injection understanding • Security operations |
| MLOps & Deployment | • Adopt CI/CD for ML pipelines • Implement progressive rollouts • Establish monitoring and alerting • Create rollback procedures • Maintain model registry |
• Kubernetes, Docker • Jenkins, GitLab CI, GitHub Actions • Kubeflow, MLflow • Prometheus, Grafana • Model registries (MLflow, SageMaker) • DevOps expertise • Container orchestration • Cloud platform proficiency (AWS, Azure, GCP) • Infrastructure as code • SRE principles |
| Monitoring & Maintenance | • Implement drift detection • Create automated retraining triggers • Establish performance baselines • Conduct regular model audits • Gather user feedback continuously |
• Evidently AI • Fiddler AI • Arthur AI • Datadog, New Relic • User feedback platforms (Pendo, Amplitude) • Production monitoring • Alert triage and response • Root cause analysis • Data science for drift analysis • User research |
| Governance & Compliance | • Create AI ethics review boards • Implement model documentation standards • Establish approval workflows • Conduct regular compliance audits • Maintain audit trails |
• Model cards frameworks • Compliance management platforms • Document management systems • Audit logging infrastructure • Regulatory compliance expertise • Technical writing • Risk assessment • Legal/policy knowledge • Cross-functional communication |
| Explainability | • Implement explanation generation • Validate explanation accuracy • Create user-facing explanations • Test explanation consistency |
• LIME, SHAP • InterpretML (Microsoft) • Alibi • Captum (PyTorch) • What-If Tool • Interpretable ML expertise • UX design for explanations • Statistical communication • Domain expertise • Human factors psychology |
Cross-Cutting Best Practices
Process:
- Shift-Left Testing: Begin testing from the design phase, not after development
- Automate Everything Testable: Manual testing doesn’t scale for AI systems that continuously evolve
- Embrace Failure: Create safe environments for discovering failure modes early
- Document Obsessively: Model cards, data sheets, decision logs create institutional memory
- Foster Cross-Functional Collaboration: QA, data science, security, and domain experts must work together
Tooling:
- Build Don’t Buy (Selectively): Use commercial tools where possible, but custom test harnesses may be needed for domain-specific validation
- Integrate into Existing Workflows: AI testing tools should fit into CI/CD, not create parallel processes
- Prioritize Observability: You can’t test what you can’t measure
- Maintain Tool Portfolio: Different testing phases require different tools; no single solution handles everything
Skills:
- Invest in Training: Gartner predicts 80% of the workforce will need upskilling by 2027 due to generative AI
- Hire Diverse Teams: Testing for bias requires diverse perspectives
- Bridge Silos: Create roles that span traditional boundaries (MLOps engineers, AI QA specialists)
- Cultivate Domain Expertise: Technical testing without domain knowledge misses critical failures
7. Limitations and Challenges When Testing AI Systems at Scale
Challenge 1: The Combinatorial Explosion Problem
The Issue: AI systems operate across virtually infinite input spaces. A chatbot might encounter millions of unique conversational contexts. An autonomous vehicle must handle countless combinations of weather, traffic, and road conditions.
Impact: Comprehensive testing becomes computationally infeasible. You cannot test all scenarios.
Mitigation Strategies:
- Focus on high-risk scenarios through threat modeling
- Use statistical sampling techniques to achieve representative coverage
- Implement fuzzing and automated adversarial test generation
- Prioritize edge cases identified through production monitoring
- Leverage synthetic data generation for rare but critical scenarios
Reality Check: Even with sophisticated approaches, you will deploy with untested edge cases. The question becomes: how do you detect and respond when the system encounters them in production?
Challenge 2: Model Drift and Temporal Instability
The Issue: AI models trained on historical data become stale as the world changes. A fraud detection model trained in 2023 may fail against 2025 fraud tactics. Customer preferences shift. Language evolves. Market dynamics change.
Impact: Models degrade over time even without code changes. A 2024 Qentelli report found 57% of organizations struggle with shifting requirements and frequent model updates.
Mitigation Strategies:
- Implement continuous monitoring for data drift and concept drift
- Establish automated retraining pipelines with human-in-the-loop validation
- Create champion/challenger frameworks to compare models
- Set performance thresholds that trigger retraining
- Maintain baseline datasets to detect degradation
Reality Check: Drift is inevitable, not exceptional. Testing frameworks must assume change rather than stability.
Challenge 3: The Explainability-Performance Trade-off
The Issue: The most accurate models (deep neural networks, large ensembles) are often the least explainable. Simpler, interpretable models (decision trees, linear regression) sacrifice performance.
Impact: In regulated industries or high-stakes applications, you may not be able to deploy your best-performing model because you can’t explain its decisions.
Mitigation Strategies:
- Define explainability requirements upfront in the design phase
- Use post-hoc explanation techniques (LIME, SHAP) for complex models
- Establish minimum performance thresholds for interpretable models
- Create tiered approaches: complex models with human oversight, simple models for autonomous decisions
- Document and test explanation accuracy alongside model accuracy
Reality Check: There’s no free lunch. Testing must evaluate both prediction accuracy and explanation quality.
Challenge 4: Resource Constraints and Cost Management
The Issue: Comprehensive AI testing is expensive. Training large models costs thousands to millions of dollars. Running extensive test suites consumes significant compute resources. Specialized skills command premium salaries.
Impact: Testing budgets often get cut first when projects face pressure, creating technical debt and increasing production risk.
Mitigation Strategies:
- Implement risk-based testing: allocate resources proportional to potential harm
- Use smaller surrogate models for rapid iteration during development
- Leverage transfer learning to reduce training costs
- Implement efficient CI/CD pipelines that parallelize tests
- Utilize spot instances and cost-optimization strategies for cloud resources
- Invest in automation to reduce ongoing manual testing costs
Reality Check: Undertesting to save budget is penny-wise and pound-foolish. The cost of a production failure often exceeds the entire testing budget.
Challenge 5: Lack of Ground Truth in Production
The Issue: In development, you have labeled datasets to validate against. In production, true labels may arrive late or never.
Impact: Traditional accuracy metrics become impossible to calculate in real-time production scenarios.
Mitigation Strategies:
- Implement proxy metrics that correlate with true accuracy
- Create delayed validation loops that collect ground truth over time
- Use confidence scores and uncertainty quantification to flag questionable predictions
- Establish human-in-the-loop review for high-uncertainty cases
- Monitor downstream effects such as user satisfaction or conversion rates
Reality Check: You’re often flying partially blind in production. Robust monitoring and feedback loops are essential.
Challenge 6: Adversarial Sophistication
The Issue: Attackers are increasingly sophisticated in exploiting AI systems. Prompt injection attacks evolve faster than defenses. Adversarial examples fool computer vision systems.
Impact: Security testing becomes an arms race where yesterday’s defenses are insufficient for tomorrow’s threats.
Mitigation Strategies:
- Establish continuous red team testing programs
- Monitor adversarial research and incorporate new attack vectors into test suites
- Implement defense-in-depth with multiple protection layers
- Use adaptive defenses that evolve alongside threats
- Participate in industry information sharing
- Consider bug bounty programs for external testing
Reality Check: You will never achieve perfect security. Focus on detection and response alongside prevention.
Challenge 7: Regulatory Uncertainty and Compliance Complexity
The Issue: AI regulations are evolving rapidly and inconsistently across jurisdictions.
Impact: Testing requirements aren’t standardized. Compliance in one jurisdiction may fail in another.
Mitigation Strategies:
- Design for the strictest applicable requirements
- Implement flexible testing frameworks for evolving regulations
- Maintain comprehensive documentation and audit trails
- Engage legal counsel early
- Participate in standards bodies (ISO, IEEE, NIST)
Reality Check: Compliance is a moving target. Build adaptable testing frameworks.
Challenge 8: Organizational Silos and Cultural Resistance
The Issue: AI testing requires collaboration across traditionally siloed teams.
Impact: Testing gaps emerge due to unclear ownership and skill mismatches.
Mitigation Strategies:
- Establish cross-functional AI Centers of Excellence
- Create bridging roles such as MLOps engineers and AI QA specialists
- Implement shared KPIs that incentivize collaboration
- Invest in cross-disciplinary training programs
- Secure executive sponsorship to drive cultural change
Reality Check: Technology is easier to fix than people and processes. Organizational transformation is essential.
8. The Future Evolution of AI Testing
Near-Term Evolution (2025-2027)
Agentic AI Testing Systems: The most significant trend emerging in 2025 is agentic AI—AI systems that can take actions autonomously to accomplish goals. Multiple industry experts, including Jonathan Wright and Jason Arbon, predict agentic AI will fundamentally redefine testing paradigms.
Agentic testing systems will:
- Autonomously generate test cases from requirements
- Self-heal test scripts when applications change
- Make intelligent decisions about test prioritization
- Investigate failures and provide root cause analysis
- Continuously optimize test coverage
Predictive Incident Management: AI is flipping traditional reactive testing on its head. Platforms like Dynatrace, Datadog, and New Relic are integrating AI models that predict incidents hours before they manifest, based on subtle pattern changes in logs, metrics, and traces.
AI will predict:
- Which commits are most likely to introduce bugs
- When performance degradation will cross critical thresholds
- Which test cases are most likely to fail in the next run
- What dependencies pose the highest risk
Shift-Right Testing Maturity: While “shift-left” testing (testing earlier in development) has been the mantra, AI enables sophisticated “shift-right” testing directly in production environments.
- Chaos engineering becomes AI-orchestrated
- Continuous experimentation with live production traffic
- Automated detection of emerging failure modes
- Self-healing production systems
Standardization and Certification: Organizations such as ISO and IEEE are actively developing AI testing standards. The ISTQB (International Software Testing Qualifications Board) now offers a “Certified Tester AI Testing” certification, establishing baseline competencies.
By 2027, expect:
- Industry-standard AI testing frameworks
- Regulatory requirements for AI testing documentation
- Third-party AI testing certification services
- Insurance requirements for AI testing validation
Medium-Term Evolution (2028-2030)
Compositional Testing for Multi-Agent Systems: As AI systems evolve from single models to orchestrated multi-agent ecosystems, testing must validate not just individual agents but their collective behavior and interactions.
- Inter-agent communication protocols
- Emergent behaviors arising from agent interactions
- System-level properties beyond individual agent capabilities
- Dynamic agent composition and substitution
Federated Testing Across Organizations: Privacy-preserving testing techniques enable organizations to collaborate on AI testing without sharing sensitive or proprietary data.
- Federated learning for bias detection across institutions
- Differential privacy in test result sharing
- Collaborative red team exercises
- Industry-wide adversarial attack databases
Hardware-Software Co-Testing: As specialized AI hardware such as neuromorphic chips and quantum processors matures, AI testing will increasingly span both software and hardware dimensions.
- Hardware-aware performance testing
- Chip-specific optimization validation
- Power efficiency and thermal testing
- Hardware failure mode analysis
Continuous Ethical Auditing: Automated tools will continuously assess AI systems for ethical compliance throughout their operational lifecycle.
- Real-time bias drift detection
- Fairness degradation monitoring
- Privacy leak detection
- Automated impact assessments
Long-Term Evolution (2030+)
AI Testing AI: We are approaching a future where AI systems design and execute test suites for other AI systems, creating a meta-level of testing intelligence. This evolution raises profound technical and governance questions.
- How do we validate the testing AI itself?
- Can AI-generated security assessments be trusted?
- What is the appropriate role of human oversight in fully autonomous testing systems?
Provable AI Safety: Formal verification techniques from traditional software engineering will mature and adapt for AI systems, enabling stronger guarantees about behavior and safety.
- Mathematical proofs of safety properties
- Bounded guarantees on model behavior
- Certified robustness against adversarial attacks
- Verifiable compliance with ethical constraints
Quantum AI Testing: As quantum computing begins to influence AI architectures, entirely new testing paradigms will be required to validate correctness, performance, and claimed advantages.
- Testing quantum-enhanced AI models
- Validating quantum advantage claims
- Debugging quantum–classical hybrid systems
Neuromorphic Testing Paradigms: If AI architectures shift toward brain-inspired neuromorphic computing, testing approaches must evolve to address fundamentally different computational and failure characteristics.
- Validation of spike-based neural networks
- Testing event-driven, asynchronous processing models
- Identification and mitigation of novel failure modes
Biological-Digital Interface Testing: As AI systems increasingly interface directly with biological systems—such as brain-computer interfaces and synthetic biology—testing will extend beyond software into human and biological safety domains.
- Biocompatibility and safety testing
- Long-term effects and stability validation
- Ethical implications of human augmentation
9. NStarX Perspective: Future Considerations for Testing AI Systems
At NStarX, we believe the future of AI testing must address several critical dimensions that current practices underserve:
1. Testing for Data Sovereignty and Federated AI
As a leader in federated learning and data sovereignty solutions, NStarX recognizes a fundamental gap in current testing frameworks: they assume centralized data and model access. The future requires testing methodologies that respect distributed ownership and regulatory boundaries.
Validate Federated Learning Integrity:
- Test that local model updates do not compromise global model performance
- Verify privacy preservation across distributed training
- Validate convergence in non-IID (non-identically distributed) data scenarios
- Ensure Byzantine-robust aggregation against malicious nodes
Multi-Stakeholder Testing:
- Enable healthcare consortiums to test AI models without sharing patient data
- Allow financial institutions to collaboratively test fraud detection while maintaining competitive confidentiality
- Facilitate cross-border AI testing that respects data sovereignty regulations
Real-World Impact: Healthcare providers using NStarX’s federated learning platform must validate AI models across institutions while maintaining HIPAA compliance. Federated testing protocols enable rigorous validation while preserving data sovereignty.
2. Service-as-Software Testing Paradigm
NStarX’s Service-as-Software delivery model challenges traditional testing assumptions. When AI capabilities are delivered as managed services rather than deployed software, testing must evolve accordingly.
Continuous Service Validation:
- Real-time testing of service endpoints
- SLA monitoring and compliance testing
- Multi-tenant isolation and security testing
- Zero-downtime update validation
Consumer-Centric Testing:
- Test from the consumer’s perspective, not just the provider’s
- Validate API contracts and backward compatibility
- Ensure consistent behavior across service versions
- Test graceful degradation when services are unavailable
3. Testing AI Platforms, Not Just Models
The AI industry is shifting from standalone models to comprehensive platforms such as NStarX’s DLNP (Data Lake and Neural Platform). Testing must address platform-wide behavior, not isolated components.
Platform-Level Concerns:
- Interoperability between platform components
- Data lineage and governance across the platform
- Security at platform boundaries, not just model endpoints
- Performance of orchestrated workflows involving multiple AI services
Ecosystem Testing:
- Third-party integration validation
- Plugin and extension testing frameworks
- Cross-platform compatibility (cloud, edge, on-premises)
4. Domain-Specific Testing Frameworks
Generic AI testing frameworks often miss critical domain-specific requirements. NStarX operates across multiple industries, each demanding specialized testing approaches.
Healthcare AI Testing:
- Clinical workflow integration validation
- Medical terminology accuracy testing
- Regulatory compliance (FDA, HIPAA, HITECH)
- Patient safety impact analysis
- Clinical decision support transparency
Financial Services AI Testing:
- Regulatory compliance (Dodd-Frank, MiFID II, Basel III)
- Explainability for loan denials and credit decisions
- Market manipulation detection
- Anti-money laundering effectiveness
- Algorithmic trading safety limits
Manufacturing AI Testing:
- Real-time control system validation
- Safety-critical system certification
- Predictive maintenance accuracy
- Quality control integration
- Human-robot collaboration safety
Media and Entertainment AI Testing:
- Content recommendation quality and diversity
- Copyright and IP compliance
- Content moderation effectiveness
- Deepfake detection accuracy
- Bias in representation and visibility
5. Testing for AI Democratization
NStarX’s mission includes democratizing AI across organizations with varying technical maturity.
No-Code / Low-Code Testing Tools:
- Enable business users to validate AI behavior without coding
- Natural language test case definition
- Visual testing workflows
- Automated report generation in business terminology
Interpretable Test Results:
- Translate technical metrics into business impact
- Provide actionable recommendations, not just statistics
- Visualize model behavior for non-technical stakeholders
6. Testing for Sustainable AI
Carbon Footprint Metrics:
- Energy consumption during training and inference
- CO2 equivalent emissions
- Comparative efficiency across model architectures
- Trade-offs between accuracy and environmental impact
Resource Optimization:
- Test model compression techniques (quantization, pruning, distillation)
- Validate edge deployment reducing cloud compute requirements
- Assess hardware utilization efficiency
7. Human-in-the-Loop Testing at Scale
Collaboration Quality Metrics:
- Time to decision with AI assistance vs. without
- Accuracy improvement from AI recommendations
- User confidence and trust in AI outputs
- Cognitive load and user experience
Error Recovery Testing:
- How effectively humans catch AI mistakes
- User ability to override AI decisions
- False confidence rates in incorrect AI outputs
8. Testing for Ethical AI Evolution
Value Alignment Testing:
- Verify alignment with organizational values during adaptation
- Test for value drift during continuous learning
- Validate ethical incorporation of human feedback
Transparency and Accountability:
- Automated audit trail generation for AI decisions
- Explainability preservation across model updates
- Accountability attribution in multi-AI interactions
9. Testing Infrastructure as Code
Version Controlled:
- Test suites, data, and configurations in Git
- Reproducible testing environments
- Infrastructure as code for testing platforms
Automated and Integrated:
- CI/CD pipelines with AI testing gates
- Automated rollback on test failures
- Progressive deployment with automated validation
10. The Testing Workforce of Tomorrow
New Hybrid Roles:
- AI Quality Engineers
- Federated Learning Validators
- AI Ethics Auditors
- MLOps Reliability Engineers
Continuous Learning Culture:
- Investment in training and upskilling
- Cross-functional rotation programs
- Industry certification support
- Academic partnerships for advanced research
10. References
Academic and Research Organizations
- Stanford Human-Centered AI (2025). “AI Index Report 2025 – Documented AI Safety Incidents.” Stanford University. https://aiindex.stanford.edu/
- International Software Testing Qualifications Board (ISTQB). “Certified Tester AI Testing Certification.” https://www.istqb.org/
- Consortium for Information & Software Quality (2022). “The Cost of Poor Software Quality in the US: A 2022 Report.” CISQ.
- Deloitte (2024). “State of Gen AI Q4 2024 Report – GenAI Initiatives ROI Expectations.” Deloitte Insights. https://www2.deloitte.com/us/en/insights.html
Industry Testing Tools and Platforms
- testRigor. “AI-Based Test Automation Tool.” https://testrigor.com/
- ACCELQ. “Best AI Testing Frameworks for Smarter Automation in 2025.” https://www.accelq.com/blog/ai-testing-frameworks/
- DigitalOcean. “12 AI Testing Tools to Streamline Your QA Process in 2025.” https://www.digitalocean.com/resources/articles/ai-testing-tools
- GeeksforGeeks. “Top 15 AI Testing Tools for Test Automation (2025 Updated).” https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/websites-apps/top-ai-testing-tools-for-test-automation/
- Testmo. “10 Essential Practices for Testing AI Systems in 2025.” https://www.testmo.com/blog/10-essential-practices-for-testing-ai-systems-in-2025/
- TestGuild. “12 Best AI Test Automation Tools for 2026: The Third Wave.” https://testguild.com/7-innovative-ai-test-automation-tools-future-third-wave/
- Rainforest QA. “The top 9 AI testing tools (and what you should know).” https://www.rainforestqa.com/blog/ai-testing-tools
- Code Intelligence. “Top 18 AI-Powered Software Testing Tools in 2024.” https://www.code-intelligence.com/blog/ai-testing-tools
- Early Blog. “Top 12 AI Test Automation Tools for Smarter Software Testing in 2025.” https://www.startearly.ai/post/top-12-ai-test-automation-tools
Case Studies and ROI Research
- Beam AI. “Why 42% of AI Projects Show 0 ROI (And How to Be in the 58%).” https://beam.ai/agentic-insights/why-42-of-ai-projects-show-zero-roi
- Notch. “AI ROI Case Studies: Learning from Leaders.” https://wearenotch.com/blog/ai-roi-case-studies/
- Nielsen. “The ROI of AI – Google Marketing Mix Modeling Case Study.” https://www.nielsen.com/insights/2025/google-mmm-case-study/
- AI Multiple. “AI Agent Performance: Success Rates & ROI Research.” https://research.aimultiple.com/ai-agent-performance/
- AiPromptsX. “AI in Business: Real Case Studies with Proven ROI (2025).” https://aipromptsx.com/blog/ai-in-business-case-studies
- Leanware. “Practical AI Case Studies with ROI: Real-World Insights.” https://www.leanware.co/insights/ai-use-cases-with-roi
- Agility at Scale. “Proving ROI – Measuring the Business Value of Enterprise AI.” https://agility-at-scale.com/implementing/roi-of-enterprise-ai/
AI Failures and Incidents
- DigitalDefynd. “Top 40 AI Disasters [Detailed Analysis][2025].” https://digitaldefynd.com/IQ/top-ai-disasters/
- Martsinkevich, G. (2025). “13 AI Disasters of 2024.” Medium. https://medium.com/@georgmarts/13-ai-disasters-of-2024-fa2d479df0ae
- Responsible AI Labs. “AI Safety Incidents of 2024: Lessons from Real-World Failures.” https://responsibleailabs.ai/knowledge-hub/articles/ai-safety-incidents-2024
- CIO Magazine. “10 famous AI disasters.” https://www.cio.com/article/190888/5-famous-analytics-and-ai-disasters.html
- Adversa AI. “Top AI Security Incidents of 2025 Revealed.” https://adversa.ai/blog/adversa-ai-unveils-explosive-2025-ai-security-incidents
- MIT Technology Review. “The biggest AI flops of 2024.” https://www.technologyreview.com/2024/12/31/1109612/biggest-worst-ai-artificial-intelligence-flops-fails-2024/
- CO/AI. “The biggest AI failures of 2024 point exactly to where it needs most improvement.” https://getcoai.com/news/the-biggest-ai-failures-of-2024-point-exactly-to-where-it-needs-most-improvement/
- Curiosity AI (2025). “When AI Goes Wrong: The Shocking Reality of Artificial Intelligence Failures in 2025.” Medium. https://medium.com/@curiosityai/when-ai-goes-wrong-the-shocking-reality
- Magai. “Real-World AI Testing: Challenges and Solutions.” https://magai.co/ai-testing-challenges-solutions/
- AIBMag. “AI Case Studies Explained: Success, Failure & Lessons.” https://www.aibmag.com/ai-business-case-studies-and-real-world-enterprise-use-cases
Best Practices and Frameworks
- SmartDev. “AI Model Testing: The Ultimate Guide in 2025.” https://smartdev.com/ai-model-testing-guide/
- Orq.ai. “Managing the AI Lifecycle in 2025: A Comprehensive Guide.” https://orq.ai/blog/managing-the-ai-lifecycle
- Testlio. “AI in Software Testing: Actionable Advice for 2025.” https://testlio.com/blog/artificial-intelligence-in-software-testing/
- BugBug. “AI in Software Testing: A Practical Guide.” https://bugbug.io/blog/test-automation/ai-in-software-testing/
- Practical DevSecOps. “OWASP AI Testing Guide 2025.” https://www.practical-devsecops.com/owasp-ai-testing-guide-explained/
- TestQuality. “How AI is Transforming Software Testing in 2025.” https://testquality.com/how-ai-is-transforming-software-testing/
- Qodo. “Best Practices for Testing AI Applications.” https://www.qodo.ai/blog/testing-ai-applications-best-practices/
- Tredence. “Understanding AI Lifecycle: From Data Prep to Model Maintenance.” https://www.tredence.com/blog/ai-lifecycle
Industry Trends and Predictions
- TestGuild. “8 Automation Testing Trends for 2025 (Agentic AI).” https://testguild.com/automation-testing-trends/
- Medium – Ram Milan. “Top AI Trends in DevOps for 2025.” https://medium.com/@rammilan1610/top-ai-trends-in-devops-for-2025
- Global App Testing. “5 Generative AI Testing Tools To Consider in 2025.” https://www.globalapptesting.com/blog/generative-ai-testing-tools
Conclusion
Testing AI systems is not an extension of traditional software testing—it is a fundamentally new discipline requiring new methodologies, tools, skills, and organizational structures. The stakes have never been higher: AI systems now make decisions affecting healthcare, finance, transportation, and countless other domains where failures can cost lives, fortunes, and trust.
The data is unambiguous: organizations that invest in rigorous, comprehensive AI testing achieve measurable ROI through reduced failures, faster deployments, and improved system performance. Those that skimp on testing face catastrophic consequences—from the 13 fatal crashes involving Tesla’s Autopilot to the $60 million failure of IBM Watson Health at MD Anderson.
As we look to the future, AI testing will evolve from reactive validation to proactive prediction, from manual execution to autonomous orchestration, and from isolated practices to ecosystem-wide collaboration. Organizations that master AI testing will not only deploy safer systems—they will move faster, innovate more boldly, and capture competitive advantages that undertested competitors cannot match.
At NStarX, we believe the path forward requires:
- Federated testing approaches that respect data sovereignty while ensuring quality
- Service-as-Software testing paradigms aligned with modern delivery models
- Domain-specific frameworks addressing healthcare, finance, and industry-specific requirements
- Human–AI collaboration testing that validates augmentation rather than replacement
- Ethical and sustainable AI validation that considers environmental and societal impact
The question is not whether to invest in AI testing—it is whether you will be among the 58% that achieve ROI or the 42% that show zero return. The answer lies in treating testing not as a cost center but as a competitive advantage, not as a final gate but as a continuous practice, and not as a purely technical challenge but as an organizational transformation.
The future of AI is not just about building smarter systems—it is about building trustworthy systems we can deploy with confidence. Rigorous testing is the foundation of that trust.